MyoGestic - Open-Source, Adaptive EMG Interface for Restoring Motor Function in Individuals with Neural Lesions
Restoring motor function in individuals with spinal cord injury (SCI), stroke, or amputation remains a significant challenge. Research shows that even without visible limb movement, spared motor neurons can still be voluntarily controlled, detectable via surface electromyography (EMG). However, existing wearable solutions lack the necessary hardware and software for intuitive use of these signals.
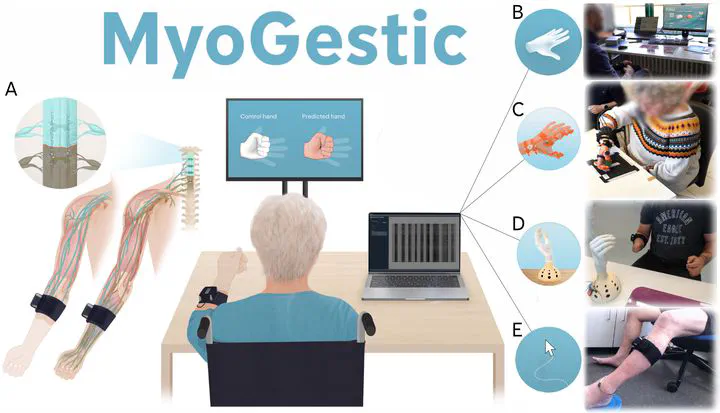
To address this, we developed MyoGestic, a system combining a wireless, high-density EMG bracelet with a novel software framework. MyoGestic enables real-time decoding of motor intent, adapting machine learning models to individual users within minutes. In tests with participants (including those with SCI, spinal stroke, and amputations), the system successfully decoded motor intent for controlling multiple degrees of freedom in real-time. Applications demonstrated included controlling a virtual hand, a wearable orthosis, a prosthesis, and a 2D cursor.
MyoGestic emphasizes user-centered design, integrating immediate feedback to refine myocontrol algorithms. The open-source framework aims to bridge research and clinical applications, advancing the development of intuitive, adaptive EMG interfaces for individuals with neural injuries.